Electrotherapy Well-being currents
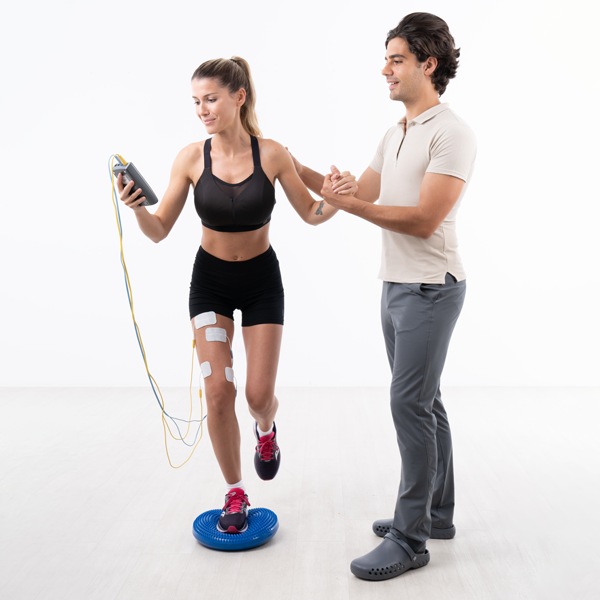

Main indications
Globus and electrotherapy
Why choose us?
Globus electrotherapy devices
60
2 independent (4 electrodes)
50-400µs
0-100mA per channel
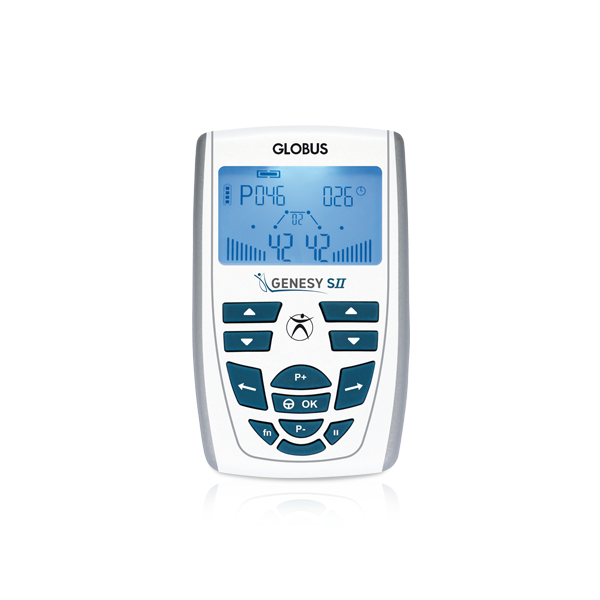

20
2 independent (4 electrodes)
50-400µs
0-100mA per channel
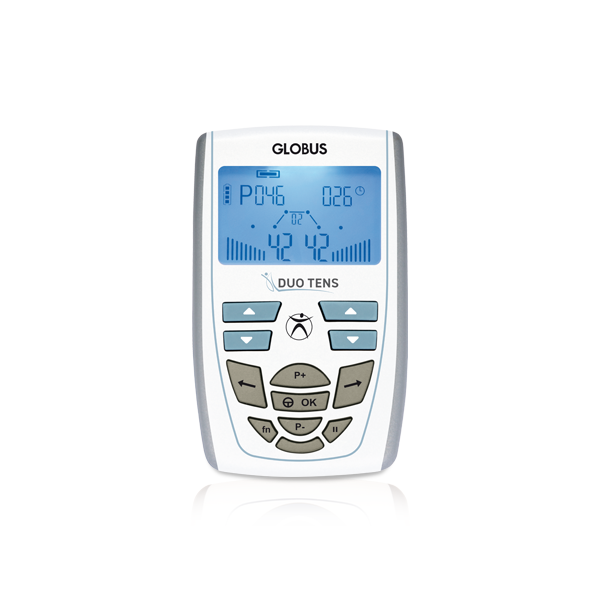

91
4 independent (8 electrodes)
40-450µs
0-120mA per channel
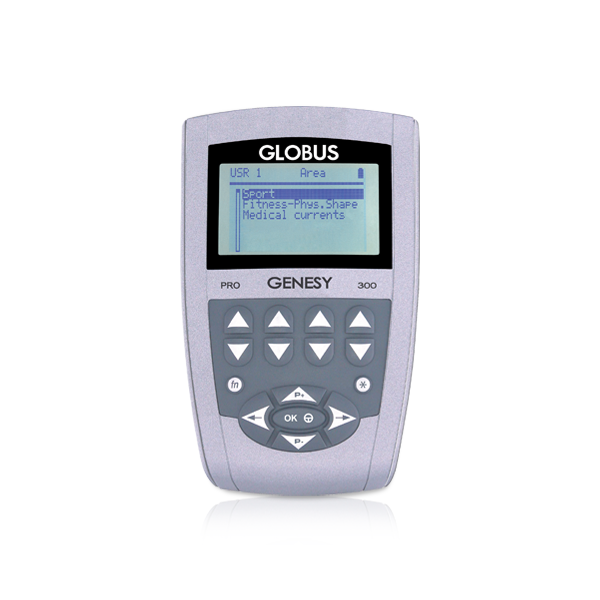

149
4 independent (8 electrodes)
40-450µs
0-120mA per channel

Globus electrotherapy accessories
TENS currents
The decrease in pain is linked to three factors: the gate control theory, endorphin secretion and different sedative effects in relation to frequency
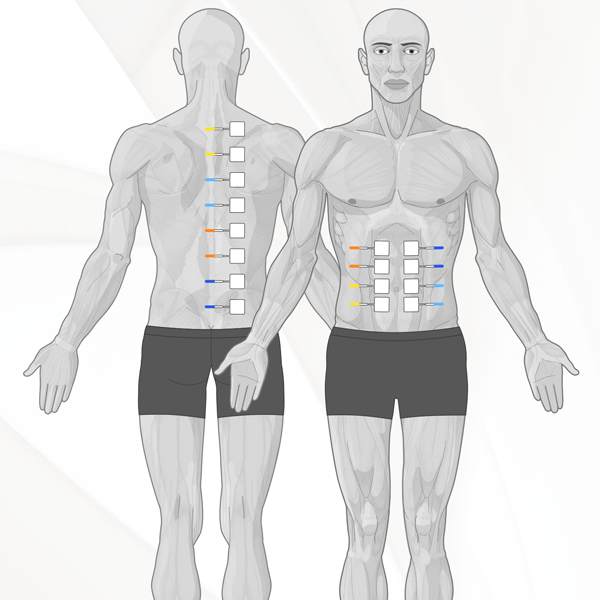
How to place the electrodes
Clinical electrotherapy studies
Satoshi Hasegawa, Masahiko Kobayashi, Ryuzo Arai, Akira Tamaki, Takashi Nakamura, Toshio Moritani
Published online: 18 February 2011
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the effectiveness of muscle electrostimulation in addition to the standard rehabilitation protocol, in muscle recovery after ACL surgery.
PROTOCOL
20 minutes of stimulation, 5 times a week for 4 weeks.
RESULTS

CONCLUSIONS
The use of muscle electrostimulation after ACL surgery helps prevent muscle atrophy by improving strength and fibre thickness.
Jan Magnus Bjordal, Mark I Johnson, Anne Elisabeth Ljunggreen
Published online: 18 February 2003
OBJECTIVE
To carry out an analysis of reviews in literature to investigate whether TENS can reduce the consumption of painkillers after surgery.
PROTOCOL
RESULTS

CONCLUSIONS
– The meta-analysis showed strong evidence that TENS reduces postoperative pain with lower analgesic intake during the first 3 days after surgery.
• The most successful parameters were with 85 Hz frequency and medium-high stimulation intensity.
Gautier Chêne, Aslam Mansoor, Bernard Jacquetin, Georges Mellier, Serge Douvier, Fabrice Sergent, Yves Aubard, Pierre Seffert
Published online: 5 July 2013
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the effectiveness of vaginal electrical stimulation performed at home in the treatment of urinary incontinence.
PROTOCOL
20-30 minutes of electrostimulation per day, 5 days a week for 10 weeks.
RESULTS

CONCLUSIONS
– The patients’ satisfaction rate was very high and the treatment was well tolerated. These factors, combined with the fact that the therapy can be carried out at home, makes electrostimulation one of the preferred interventions in the treatment of female urinary incontinence.
Harikrishna K.R. Nair
Published online: 8 May 2018
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the efficacy of microcurrents in the healing of chronic wounds (venous ulcers, diabetic ulcers, pressure sores).
PROTOCOL
20 minutes three times a day for a duration to be evaluated according to
re-epithelialisation.
RESULTS

CONCLUSIONS
Photo A. Venous ulcer (size 11×6.9 cm) in the left lower limb, persistent for more than 5 years.
Photo B. After only 4 weeks of microcurrent treatment the wound healed with complete re-epithelialisation
